Polymer compound formed by polymerization of tetrafluoroethylene
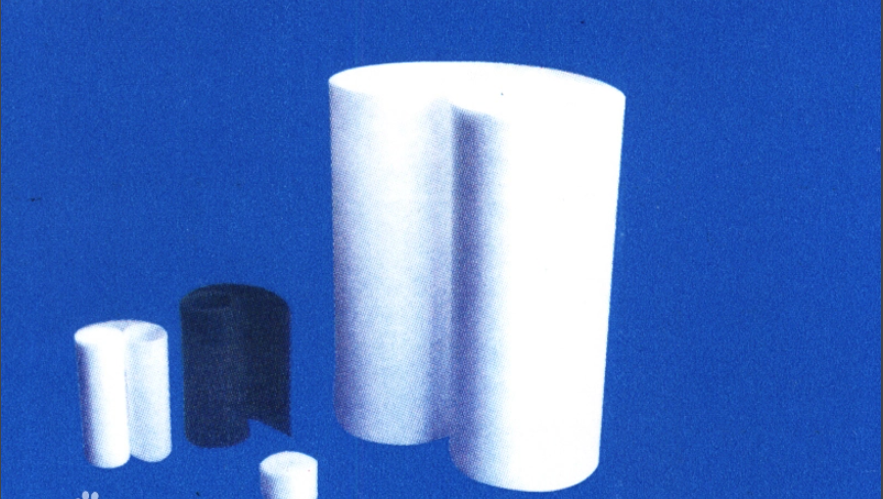
Polytetrafluoroethylene board (also known as PTFE board, Teflon board, or Teflon board) is made by molding polytetrafluoroethylene resin at room temperature, followed by sintering and cooling.
Chinese name: PTFE board, foreign name: mechanical seal, alias: PTFE board, Teflon board, Teflon board, PTFE sealing board
catalogue


1 Product Introduction
2 Purpose
3 Material advantages
4 Appearance standards
5 Technical parameters
6 Chemical formula
Product Introduction
PTFE board (also known as PTFE board, Teflon board, Teflon board) is divided into two types: molding and turning. Its products have a wide range of uses and excellent comprehensive performance: high and low temperature resistance (-192 ℃ -260 ℃), corrosion resistance (strong acid, strong alkali, aqua regia, etc.), climate resistance, high insulation, high lubrication, non adhesion, non-toxic and other excellent characteristics. Polytetrafluoroethylene (abbreviated as Teflon or [PTFE, F4]), commonly known as the "King of Plastics", has Chinese trade names such as "Teflon", "Teflon", "Teflon", "Teflon", "Teflon", "Teflon", and so on.
It is a polymer compound formed by polymerization of tetrafluoroethylene, with a simple structural formula of - [- CF2-CF2-] n -, and has excellent chemical stability Corrosion resistance (PTFE or F4 for short) is one of the most corrosion-resistant materials in the world today, known as the "King of Plastics" It is a common name for polytetrafluoroethylene, which is a plastic with the best corrosion resistance. It is not corroded by known acids, alkalis, salts and oxidants, and even aqua regia can do nothing about it. Therefore, it is named Plastic King. Except molten metal sodium and liquid fluoride, it can resist all other chemicals, and is widely used in various kinds of products that require resistance to acids, alkalis and organic solvents, sealing, high lubrication, non adhesion, electrical insulation, good anti-aging endurance, and excellent temperature resistance (it can work at a temperature of+250 ℃ to -180 ℃ for a long time). Polytetrafluoroethylene itself is not toxic to humans, but one of the raw materials used in the production process, perfluorooctanoic acid ammonium (PFOA), is believed to have carcinogenic effects.
The temperature is -20~250 ℃ (-4~+482 ° F), allowing sudden cooling and heating, or alternating cold and hot operations.
Pressure -0.1~6.4Mpa (full vacuum to 64kgf/cm2)
Its complete thermal decomposition products at around 500 degrees Celsius include tetrafluoroethylene, hexafluoropropylene, and octafluorocyclobutane, which decompose into highly corrosive fluorinated gases at high temperatures.
Its emergence has solved many problems in China's chemical, petroleum, pharmaceutical and other fields. PTFE seals, gaskets, gaskets, PTFE seals, and sealing washers are made by using suspension polymerized PTFE resin molding. Compared with other plastics, polytetrafluoroethylene has the characteristic of chemical corrosion resistance and has been widely used as a sealing and filling material.
purpose
Various types of polytetrafluoroethylene products have played a crucial role in the national economy, including chemical, mechanical, electronic, electrical, military, aerospace, environmental protection, and bridge industries.
Tetrafluoroethylene plate is suitable for temperatures ranging from -180 ℃ to+250 ℃ and is mainly used as insulation material for electrical appliances and lining for contact with corrosive media, supporting sliders, track seals, and lubricating materials. Rich cabinet furniture uses it in light industry and is widely used as anti-corrosion lining material for chemical, pharmaceutical, dye industry containers, storage tanks, reaction towers, and large pipelines; Heavy industries such as aviation and military; Mechanical, architectural, traffic bridge sliders, guide rails; Anti stick materials for printing and dyeing, light industry, textile industry, etc
Material advantages
High temperature resistance - operating temperature up to 250 ℃.
Low temperature resistance - with good mechanical toughness; Even if the temperature drops to -196 ℃, an elongation of 5% can be maintained.
Corrosion resistance - shows inertness and resistance to strong acids, alkalis, water, and various organic solvents for most chemicals and solvents.
Climate resistance - has the best aging life among plastics.
High lubrication - is the lowest friction coefficient among solid materials.
Non adhesion - refers to the minimum surface tension in solid materials, which does not adhere to any substance. Its friction coefficient for mechanical properties is extremely small, only 1/5 of that of polyethylene, which is an important feature of perfluorocarbon surfaces. Due to the extremely low intermolecular force between fluorine carbon chains, polytetrafluoroethylene is non viscous.
Non toxic - with physiological inertness, long-term implantation of artificial blood vessels and organs into the body without adverse reactions.
Electrical performance - Polytetrafluoroethylene has low dielectric constant and loss over a wide frequency range, and has high breakdown voltage, volume resistivity, and arc resistance.
Radiation resistance - Polytetrafluoroethylene has poor radiation resistance (104 rads), which can cause degradation after being subjected to high-energy radiation, resulting in a significant decrease in the electrical and mechanical properties of the polymer. The application of polytetrafluoroethylene can be processed by compression or extrusion molding; It can also be made into aqueous dispersions for coating, impregnation, or fiber making. Polytetrafluoroethylene is widely used in industries such as atomic energy, aerospace, electronics, electrical, chemical, mechanical, instrumentation, construction, textile, food, etc. as a high and low temperature resistant, corrosion-resistant material, insulation material, anti adhesive coating, etc.
Atmospheric aging resistance: radiation resistance and low permeability: long-term exposure to the atmosphere, with the surface and properties remaining unchanged.
Non combustible: Oxygen limiting index below 90.
Acid and alkaline resistance: insoluble in strong acids, alkalis, and organic solvents.
Antioxidant: Capable of withstanding strong oxidant corrosion.
Acidity and alkalinity: neutral.
The mechanical properties of polytetrafluoroethylene are relatively soft. Has very low surface energy.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (F4, PTFE) has a series of excellent performance: high temperature resistance - long-term use temperature 200-260 degrees Celsius, low temperature resistance - still soft at -100 degrees Celsius; Corrosion resistance - resistant to aqua regia and all organic solvents; Climate resistance - the best aging life in plastics; High lubrication - with the smallest friction coefficient in plastic (0.04); Non adhesive - having the minimum surface tension in a solid material without adhering to any substance; Non toxic - with physiological inertness; Excellent electrical performance, making it an ideal C-grade insulation material.
Appearance standards
(1) The color of the board is the resin natural color.
(2) The texture should be uniform, the surface should be flat, and there should be no defects such as cracks, bubbles, layering, mechanical damage, knife marks, etc.
(3) Allow for slight cloud like tightness.
(4) Allow 10 × There should be no more than one non-metallic impurity with a diameter of 0.1-0.5mm and no more than one non-metallic impurity with a diameter of 0.5-2mm on a 10cm area.
(5) The density is 2.1-2.3T/m3
technical parameter
project
Unit
Indicators
density
G/cm3
2.1-2.3
bending strength
Mpa
11-14
tensile strength
MPa
21-28
friction coefficient
/
zero point zero four
Water absorption rate
%
<0.03
Dielectric strength
KV/mm
ten
Operating temperature
℃
-180-260
Melting temperature
℃
three hundred and twenty-five
The above data can be directly applied to a large extent, but it cannot be guaranteed to be applicable to any situation. For values measured through raw materials, there may be slight differences in the performance of the finished product. Different manufacturers may also have slight differences, so material selection cannot be guaranteed.
Chemical formula
-(CF2-CF2) n - belongs to the category of polymers: polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) has a relatively large molecular weight, ranging from hundreds of thousands to over 10 million, usually in the millions (polymerization degree is in the order of 104, while polyethylene is only in 103). The general crystallinity is 90-95%, and the melting temperature is 327-342 ℃. The CF2 units in polytetrafluoroethylene molecules are arranged in a zigzag shape. Due to the slightly larger radius of fluorine atoms compared to hydrogen, adjacent CF2 units cannot be fully trans oriented, but instead form a helical twisted chain, with fluorine atoms almost covering the entire surface of the polymer chain. This molecular structure explains the various properties of polytetrafluoroethylene. When the temperature is below 19 ℃, a 13/6 helix is formed; At 19 ℃, a phase transition occurs, and the molecules slightly unravel, forming a 15/7 helix. Although the breaking of carbon carbon bonds and carbon fluorine bonds in perfluorocarbons requires energy absorption of 346.94 and 484.88kJ/mol, the depolymerization of polytetrafluoroethylene to produce 1mol of tetrafluoroethylene only requires energy of 171.38kJ. So during high-temperature cracking, polytetrafluoroethylene mainly depolymerizes to tetrafluoroethylene. The weight loss rates (%) of polytetrafluoroethylene at 260, 370, and 420 ℃ are 1% per hour, respectively × 10-4, 4 × 10-3 and 9 × 10-2. It can be seen that polytetrafluoroethylene can be used for a long time at 260 ℃. Due to the production of highly toxic by-products such as fluorophosgene and perfluoroisobutylene during high-temperature cracking, special attention should be paid to safety protection and prevent polytetrafluoroethylene from coming into contact with open flames.